Project 2 要求我们从实现一个半加器(HalfAdder)开始, 逐步实现一个全加器(FullAdder), 一个 16 位的加法器(Add16), 一个增量器(Inc) 和一个简单的算术逻辑单元(ALU).
实现时可以使用 Project 1 中实现的逻辑门.
半加器 HalfAdder
输入: a, b
输出: out, carry
其中 out = a + b, 进位存储在 carry
| a | b | sum | carry |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
容易看出 $sum=a\oplus b,\quad carry=ab$.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
CHIP HalfAdder {
IN a, b; // 1-bit inputs
OUT sum, // Right bit of a + b
carry; // Left bit of a + b
PARTS:
// Put you code here:
Xor(a=a, b=b, out=sum);
And(a=a, b=b, out=carry);
}
全加器 FullAdder
输入: a, b, c
输出: out, carry
其中, c 可以视为来自上一位加法的进位, sum = a + b + c, 进位存储在 carry 中
| a | b | c | sum | carry |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
可以使用两个半加器来实现一个全加器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
CHIP FullAdder {
IN a, b, c; // 1-bit inputs
OUT sum, // Right bit of a + b + c
carry; // Left bit of a + b + c
PARTS:
// Put you code here:
HalfAdder(a=a, b=b, sum=sum1, carry=carry1);
HalfAdder(a=c, b=sum1, sum=sum, carry=carry2);
Xor(a=carry1, b=carry2, out=carry);
}
16 位加法器 Add16
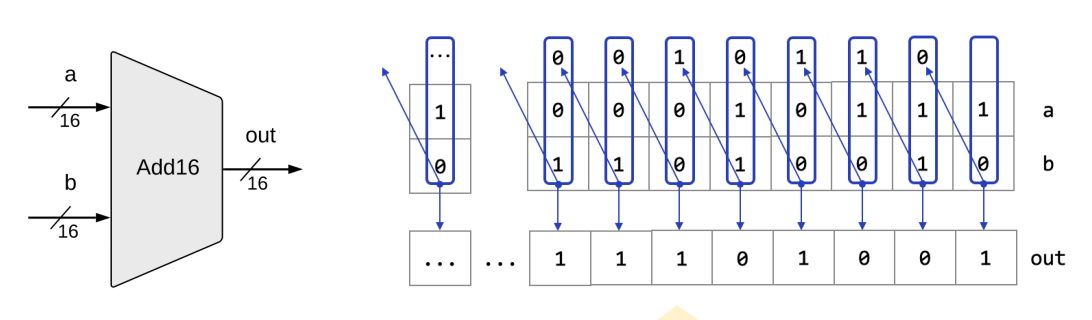
可以使用 15 个全加器来实现, 最低位使用半加器, 因为无需考虑上一位的进位.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
CHIP Add16 {
IN a[16], b[16];
OUT out[16];
PARTS:
// Put you code here:
HalfAdder(a=a[0], b=b[0], sum=out[0], carry=carry1);
FullAdder(a=a[1], b=b[1], c=carry1, sum=out[1], carry=carry2);
FullAdder(a=a[2], b=b[2], c=carry2, sum=out[2], carry=carry3);
FullAdder(a=a[3], b=b[3], c=carry3, sum=out[3], carry=carry4);
FullAdder(a=a[4], b=b[4], c=carry4, sum=out[4], carry=carry5);
FullAdder(a=a[5], b=b[5], c=carry5, sum=out[5], carry=carry6);
FullAdder(a=a[6], b=b[6], c=carry6, sum=out[6], carry=carry7);
FullAdder(a=a[7], b=b[7], c=carry7, sum=out[7], carry=carry8);
FullAdder(a=a[8], b=b[8], c=carry8, sum=out[8], carry=carry9);
FullAdder(a=a[9], b=b[9], c=carry9, sum=out[9], carry=carry10);
FullAdder(a=a[10], b=b[10], c=carry10, sum=out[10], carry=carry11);
FullAdder(a=a[11], b=b[11], c=carry11, sum=out[11], carry=carry12);
FullAdder(a=a[12], b=b[12], c=carry12, sum=out[12], carry=carry13);
FullAdder(a=a[13], b=b[13], c=carry13, sum=out[13], carry=carry14);
FullAdder(a=a[14], b=b[14], c=carry14, sum=out[14], carry=carry15);
FullAdder(a=a[15], b=b[15], c=carry15, sum=out[15], carry=carry16);
}
这里实现的是一个串行进位二进制并行加法器, 被加数和加数的各位能同时到达各位的输入端, 而各位全加器的进位输入则是按照由低位向高位逐级串行传递的.
16 位增量器 Inc16
增量器的功能很简单, 即对输入加 1.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
CHIP Inc16 {
IN in[16];
OUT out[16];
PARTS:
// Put you code here:
Add16(a=in, b[0]=true, out=out);
}
ALU
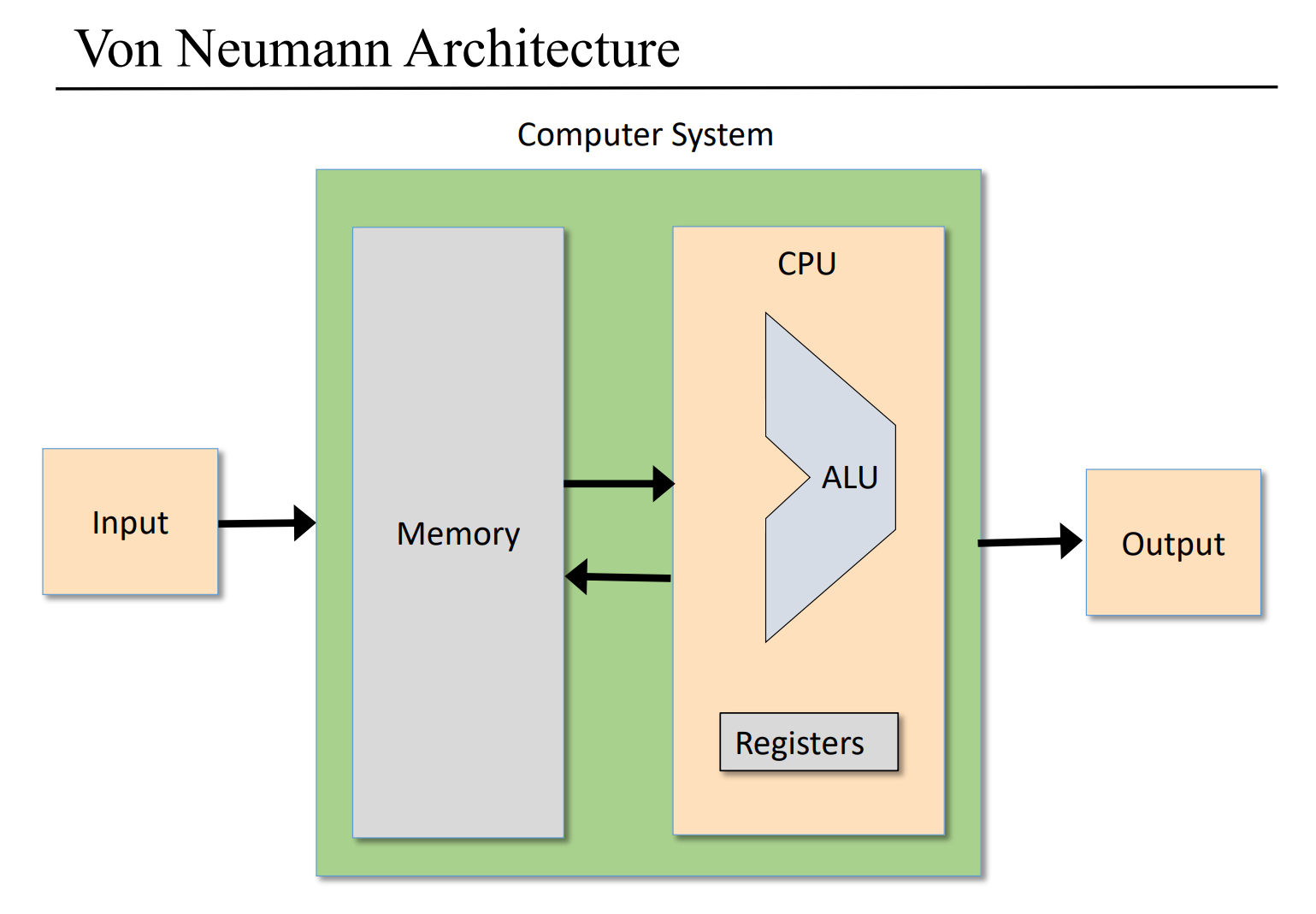
上图给出了冯·诺依曼结构的计算机体系结构, 这里要实现就是其中的 ALU 算术逻辑单元.
本课程中实现的 ALU 中包含的功能如下:
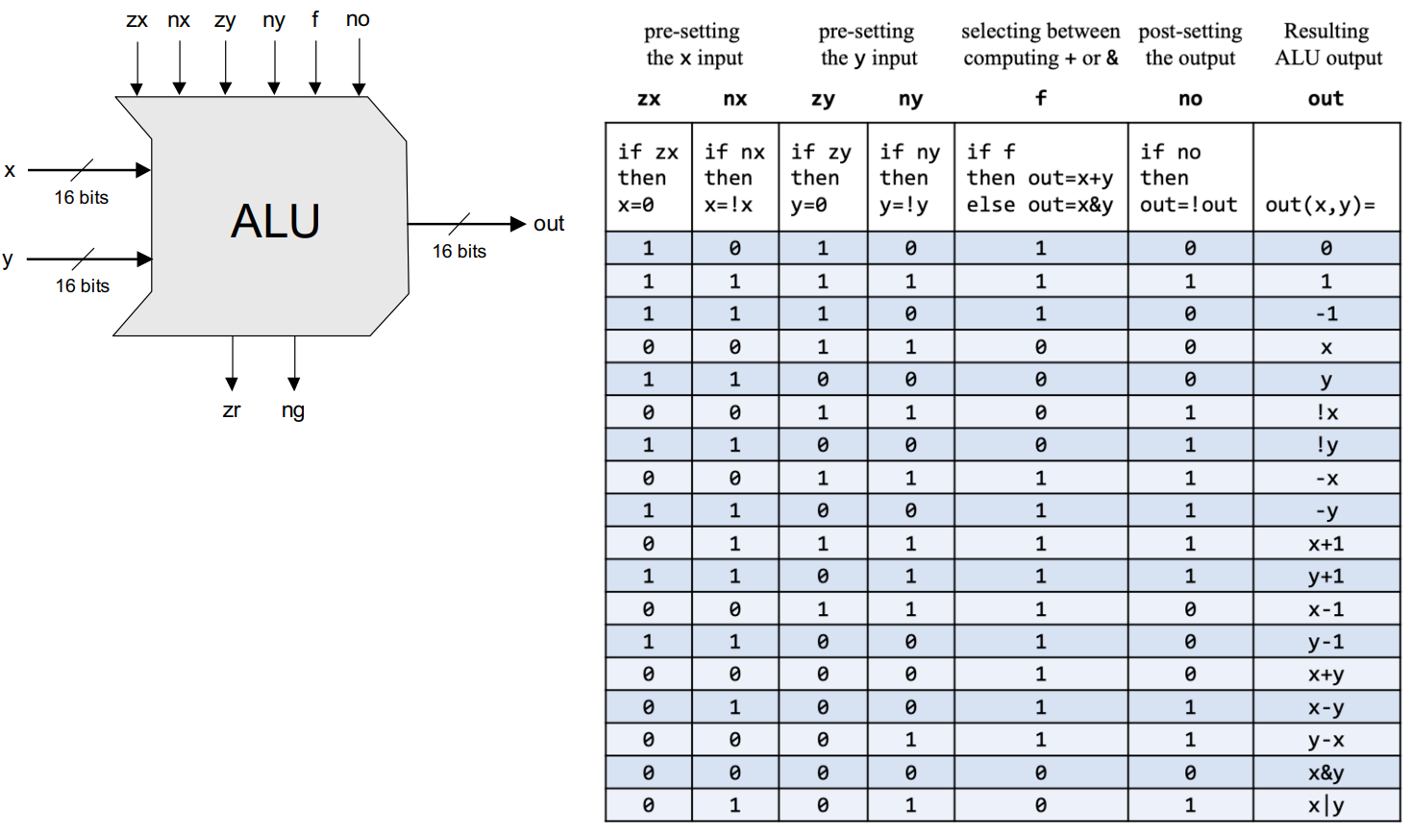
根据给出的功能表, 给出 ALU 的实现如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
CHIP ALU {
IN
x[16], y[16], // 16-bit inputs
zx, // zero the x input?
nx, // negate the x input?
zy, // zero the y input?
ny, // negate the y input?
f, // compute out = x + y (if 1) or x & y (if 0)
no; // negate the out output?
OUT
out[16], // 16-bit output
zr, // 1 if (out == 0), 0 otherwise
ng; // 1 if (out < 0), 0 otherwise
PARTS:
// Put you code here:
Mux16(a=x, b=false, sel=zx, out=x1);
Not16(in=x1, out=notx1);
Mux16(a=x1, b=notx1, sel=nx, out=x2);
Mux16(a=y, b=false, sel=zy, out=y1);
Not16(in=y1, out=noty1);
Mux16(a=y1, b=noty1, sel=ny, out=y2);
Add16(a=x2, b=y2, out=aAddb);
And16(a=x2, b=y2, out=aAndb);
Mux16(a=aAndb, b=aAddb, sel=f, out=out1);
Not16(in=out1, out=notout1);
Mux16(a=out1, b=notout1, sel=no, out[15]=ng, out[0..7]=out07, out[8..15]=out815, out=out);
Or8Way(in=out07, out=tmp1);
Or8Way(in=out815, out=tmp2);
Or(a=tmp1, b=tmp2, out=tmp3);
Not(in=tmp3, out=zr);
}